Biology Study Guide Semester 2
Section A: Scientific Processes and Introduction to Biology (Ch 1) Topics: Microscope Use, Scientific Method, Metric System 1. List the steps of the scientific method: ask question / observation develop hypothesis experiment draw conclusion 2. Understand how a controlled experiment is conducted. Sample: A scientist wants to know if Miracle Grow will increase the number of tomatoes on his tomato plants.
To tomato plant A he adds miracle grow; and to tomato plant B he does not add miracle grow. Both plants are given the same amount of light and water. After 6 weeks he counts the number of tomatoes are present on each plant. Plant A = 9 Plant B = 4 a. What is the manipulated variable in the experiment?
miracle grow b. What is the responding variable? number of tomatoes c. Which is the control group? group B. Microscope Use: a.
When first focusing the microscope, which objective do you use? scanning (4x) b. When using the high power objective, which focus knob do you use? coarse c. What are the three objectives found on the microscopes you used in class? fine adjustment d. What part of the microscope can be used to adjust the amount of light?
Metric System a. What metric system unit would be used to measure volume (such as a can of coke)? ml or liter b. What metric system unit would be used to measure the length of a room?
Terms/Concepts a. Biology the study of life b. Science gathers information about the world using obvservations and experimentation c. Hypothesis a proposed answer or explanation, a testable statement d. Controlled Experiment used to test a hypothesis, tests only one variable e. Cell the smallest unit of life f. Organism any living thing g.
Louis Pasteur disproved spontaneous generation h. Spontaneous Generation the idea that life could come from nonliving matter i. Homeostasis state of biological balance; staying the same j. Responsiveness a reaction to a stimulus k.
Reproduction making more of the same kind, either sexually or asexually l. Evolution change over time m. Energy obtained from sunlight or food, powers life processes n. Observations perceiving objects or events o. Theory a statement that explains a set of observations and is generally well accepted Section B: Cells and Cell Processes (Ch 7) Topics: Cell Structure, Organelles, Types of Cells, Cell Transport, Cell Division 1. What structure distinguishes a eukaryote from a prokaryote?

nucleus 2. What shape is a plant cell? square An animal cell?
What part of the cell is describe as selectively permeable? cell membrane 4. If you place a few drops of food coloring in a glass full of water, eventually all the water is colored. This is due to the process of diffusion 5. For each of the structures listed, indicate whether it is found in PLANTS (P), ANIMALS (A), or BOTH (B) P Chloroplasts B Cell Membrane B Nucleus P Cell Wall B Mitochondria 6.
In each of the situations pictured, indicate whether the cell will gain water, lose water, or stay the same. In each case, the cell in the beaker is 10% salt. Stays same. Cell gains water.
Cell loses water. Know the function of each of the cell organelles listed: a. Endoplasmic Reticulum intracellular highway, transport system b. Cell Membrane regulates what comes in and out of the cell c.
Ribosome makes proteins d. Lysosome contains digestive enzymes, breaks down substances e. Nucleus control center of the cell, contains DNA 8. Identify the process pictured as either mitosis, osmosis, or endocytosis Bio 1A: Also identify the phases of mitosis.
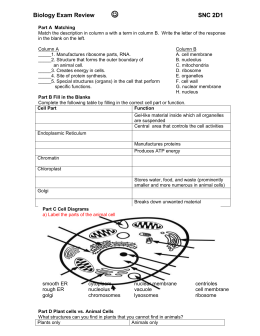
Label a plant and an animal cell: A. Cell Wall B. Cell Membrane C.
Golgi Apparatus D. Chloroplasts E.
Mitochondria AC. Cytoplasm AD. Ribosome AE.
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum BD. Nucleolus BC.
Chromosomes BE. Rough ER Section C: Evolution and Taxonomy Topics: Classification, Theory of Evolution, The Six Kingdoms 1. Define evolution: change over time 2. For each statement below, place a check next to those that provide EVIDENCE that evolution has occurred: X Animals have structures they do not use (vestigial) The same types of animals live in different parts of the world X The fossil record shows transitional species X Vertebrates have the same (or similar) internal structures, such as the bones of the forearm Every organism has unique structures unlike any other organism 3. Natural / Artificial Selection is responsible for the many different breeds of dogs.
What is an adaptation? a trait that gives an organism an advantage, or helps it survive 5. Describe how evolution would have acted on giraffes according to natural selection. Long necked animals had an advantage in that they could reach high leaves, those animals survived and passed their genes to the next generation. Short necked animals did not survive. Over time, a larger number of the population had long necks.
Who proposed the Theory of Evolution by Natural Selection? Charles Darwin 7. What is the difference between a common name and a scientific name? common names vary, scientific names have two parts and do not vary by region 8. Know the taxonomic categories used to describe how organisms are classified. KingdomPhylum , ClassOrder , FamilyGenus Species 9. What does the scientific name tell you about the organism?
Genus + Species 10. Know what types or organisms go into each of the 6 Kingdoms Animalia dogs, humans, insects Plantae trees, flowers, grass Fungi mushrooms and yeast Protista paramecium, ameba, euglena, algae Archaebacteria extremophiles Eubacteria E.coli, salmonella, streptococcus 11. Know the difference between a(n): prokaryote and eukaryote prokayotes do not have a nucleus unicellular and multicellular 1 celled; more than 1 cell heterotroph and autotroph consumes food, makes food mobile and sessile can move, cannot move 12. How did Darwin’s Theory explain the different shapes and sizes among the beaks of finches on the Galapagos? each bird was adapted to an island's particular food source 13. According to the cladogram, which two species are most closely related?
scyphozoa and cubazoa Section D: Kingdom Protista and Simple Animals Topics: Protozoans, Algae, Parasites, The Animal Kingdom, Sponges, Cnidarians 1. Label and Identify Each of the Protists Euglena Ameba Paramecium Euglena Label A. Contractile vacuole D. Cell membrane (or pellicle) E. Chloroplasts AB. Nucleus Ameba Label A. Cell membrane B.
Contractile vacuole D. Pseudopodia E. Food vacuole Parmecium Label A.
Biology 2nd Semester Final Study Guide Answers
Macronucleus B. Micronucleus C. Oral groove (or mouth pore) D. Contractile vacuole 2.
What is the function of the: Chloroplast photosynthesis Contractile Vacuole removes excess water Micronucleus involved in sexual reproduction Food Vacuole digests food Pseudopodia 'false feet', extensions of cytoplasm used for movement and catching food Pellicle stiff membrane surrounding euglena Eyespot detects light 3. How do each of these protists move? Euglena flagella Paramecium cilia Ameba pseudopodia 4. Animal-Like Protists are called protozoa 5.
To what KINGDOM do the ameba, euglena and paramecium belong? Protista 6. Check each organism if it is UNICELLULAR X Paramecium Hydra Sponge Roundworm X Ameba 7. How does a person get malaria?
getting bitten by a mosquito, which transmits the protist plasmodium into the blood 8. Where are most protozoans found? in water 9. What organisms belong to the PHYLUM PORIFERA? sponges 10.
Some animals are asymmetrical, what are the two types of symmetry found in other animals? Bilateral and radial 11. On the animal below, label the dorsal ( B), ventral ( C), posterior ( D) and anterior ( A) sides 12.
Unlike other animals, sponges do NOT have (check all that apply) X symmetry cells X tissues the ability to reproduce 13. Can sponges reproduce asexually? yes Sexually? yes 14. What is a hermaphrodite? can produce both sperm and eggs 15. What does “sessile” mean?
lives attached to a surface, does not move 16. Name an organism that is sessile: sponge, hydra, coral, anemone 17. To be classified into the animal kingdom, organisms must be (check all that apply) X Multicellular X Heterotrophic Hermaphroditic Mobile 18. Cnidarians use their tentacles for: capturing prey 19. Which of the following forms is the medusa (first)? Which is the polyp (second)?
Section D: Invertebrates Topics Covered: Roundworms, Flatworms, Mollusks, Annelids, Arthropods 1. What is regeneration?
regrowth of body parts 2. Roundworms belong to the Kingdom Animalia and the Phylum Nematoda 3. How might a person contract a tapeworm? eating contaminated food 4.
Where does a parasitic tapeworm live in the body? blood / intestine / brain 5. What is the intermediate host of the schistosoma worm?
snail How would a person contract schistosomiasis? stepping on snails or wading in water where snails live 6. Flatworms, such as the planarian, belong to the Kingdom Animalia and the Phylum Platyhelminthes 7. What Phylum includes all the segmented worms, like a leech or earthworm? Annelida 8.
What group of animals is characterized by an exoskeleton? Arthropods 9. What are mandibles?
chewing mouthparts that open from side to side 10. What animal has suckers, a beak, and a fin (most of you dissected it in class) squid 11.
The digestive tract of an earthworm includes the following structures. Place them in the correct order. 2 Pharynx 4 Gizzard 5 Intestine 1 Mouth 3 Crop 6 Anus 12. In most animals, the tube that connects the mouth to the stomach is the esophagus 13. Which of those structures grinds the food? gizzard Which stores food? crop Which is a muscle to help suck food (soil) in?
pharynx 14. The arrow on the drawing points to the clitellum What is the function of the structure? reproduction 15. What are the three parts of the insect body plan?
head, thorax, abdomen 16. How many legs does an insect have?
6 How many legs does a spider have? What is the function of the “foot” of the mollusk?
movement 18. Do insects have antennae?
yes Do spiders? no Do crustaceans have antennae? no 19. What was the stiff shell-like structure you removed from the squid during the dissection? pen 20. For each of the pairs, circle the set that is most closely related Always look for the two that are in the same taxon (group) a.
Spiders & scorpions - both are chelicerates b. Spiders & crabs a. Sea anemone & sponge b.
Jellyfish & hydra - both are cnidarians a. Earthworm & leech - both are annelida b.
Flatworm & roundworm a. Crab & lobster - both are crustaceans b. Lobster & millipede a. Squid & jellyfish b. Squid & snail - both are mollusks 21.
Identify the following organisms (mollusk, tapeworm, annelid, flatworm, cnidarian (hydra), crustacean).crustacean.flatworm.hydra.mollusk.tapeworm.annelid 22. On the Crayfish, identify the Antenna - attached to head Cheliped - claws Cephalothorax - front section of the body Abdomen - back section Walking Legs - larger, in the front Swimmerets - smaller, attached to abdomen 23. Of all the phyla, which contains the largest number of species? arthropoda 24. The tentacles of a cephalopod are used for what purpose? capturing food 25. On the picture of the squid, identify the: Eyes Tentacle Arm Fin Mouth 26.
Check the box if it applies to the organism: Crustacean Spider Insect Has antennae X X Member of Phylum Arthropoda X X X Has 3 body segments X Has 2 body segments, one being a cephalothorax X X Has chelicerae X 27. What is metamorphosis? changes that insects and other organisms go through as they age, sometimes resulting in dramatic changes, such as a caterpillar becoming a butterfly Bio 1A also has additional anatomy labeling: squid, hydra, sponge, crayfish, earthworm.